GTU MCWC (3170710) W-2023 Paper Solution
Q.1(a) Explain LAN, MAN, and WAN. (3 Marks)
1. LAN (Local Area Network):
Definition:
A network that connects computers within a small area like a home, school, or office.
Features:
High-speed data transfer (up to 1 Gbps or more).
Limited geographical range, usually a few hundred meters.
Uses Ethernet or Wi-Fi for connectivity.
Uses:
File and resource sharing among devices.
Connecting office devices like printers and servers.
2. MAN (Metropolitan Area Network):
Definition:
A network that connects multiple LANs within a city or a large campus.
Features:
Coverage of several kilometers.
Often uses high-speed fiber-optic cables.
Managed by service providers.
Uses:
Enables connectivity between offices in a city.
Supports regional e-governance systems.
3. WAN (Wide Area Network):
Definition:
A network that spans vast areas, such as countries or continents, connecting multiple LANs and MANs.
Features:
Relies on satellites, undersea cables, and the Internet.
Slower speed compared to LAN due to long distances.
Involves high costs.
Uses:
Facilitates global communication (e.g., Internet).
Used by multinational companies for data exchange.
Q.1(b) Differentiate Circuit Switching and Packet Switching. (4 Marks)
| Aspect | Circuit Switching | Packet Switching |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Establishes a dedicated path for communication. | Data is divided into packets sent independently. |
| Connection Type | Connection-oriented. | Connectionless. |
| Data Transmission | Continuous stream. | In packets with reassembly at the destination. |
| Bandwidth Usage | Fixed for each session. | Shared among multiple users. |
| Delay | Minimal once the connection is established. | Delays due to routing and reassembly. |
| Example | Telephone calls (PSTN). | Internet, email, and video streaming. |
Q.1(c) Explain GSM architecture and the role of its components. (7 Marks)
Definition:
The GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is a digital mobile communication system widely used worldwide. It is designed to standardize cellular communication.
Features:
Provides voice and data services.
Supports international roaming.
High security using encryption and SIM authentication.
Divides areas into cells for efficient network coverage.
Uses:
Enables mobile calls and SMS.
Supports internet access through GPRS/EDGE.
Facilitates secure and reliable mobile communication.
Components and Their Roles:
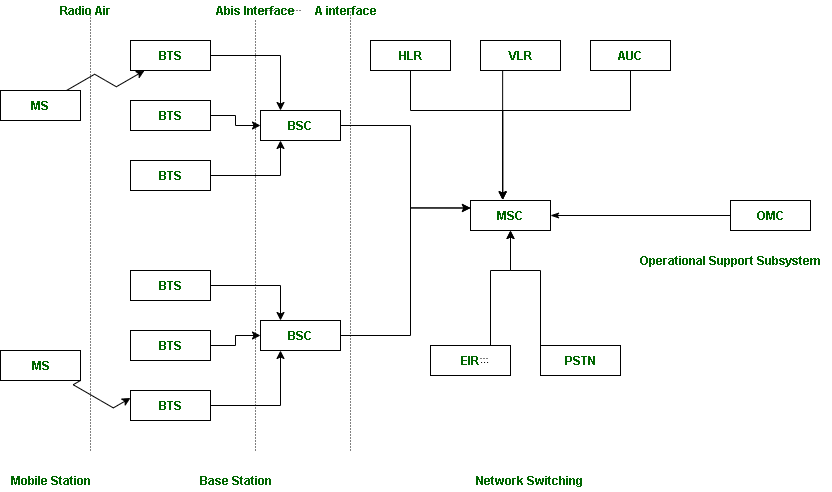 Source: geeksforgeeks
Source: geeksforgeeks
Mobile Station (MS):
User equipment like mobile phones.
Connects users to the network.
Mobile Station (MS) = Mobile Equipment(ME) + Subscriber Identity Module (SIM)
Now, these mobile stations are connected to tower and that tower connected with BTS through TRX.
Base Station Subsystem (BSS):BSS handles traffic and signaling between a mobile phone and the network switching subsystem.
Base Transceiver Station (BTS): Handles wireless communication with devices.
Base Station Controller (BSC): Manages BTS and allocates resources.
Network and Switching Subsystem (NSS):That carried out call and mobility management functions for mobile phone present in network.
Mobile Switching Center (MSC): Core component for call routing and switching.
Visitor Location Register (VLR): VLR is a database which contains the exact location of all mobile subscribers currently present in the service area of MSC.
Home Location Register (HLR):HLR is a database containing pertinent data regarding subscribers authorized to use a GSM network.
AUC : AUC stands for Authentication Center. AUC authenticates the mobile subscriber that wants to connect in the network.
EIR : EIR stands for Equipment Identity Register. EIR is a database that keeps the record of all allowed or banned in the network. If you are banned in the network then you can’t enter the network, and you can’t make the calls.
Operation and Support Subsystem (OSS):
Manages and monitors network operations.
Q.2(a) Define IMSI, IMEI, and MS-ISDN and write their use. (3 Marks)
IMSI (International Mobile Subscriber Identity):
Definition: A 15-digit unique code identifying a mobile subscriber in a network.
Use: Authentication and tracking within cellular networks.
IMEI (International Mobile Equipment Identity):
Definition: A unique 15-digit number assigned to every mobile device.
Use: Identifies the handset and blocks stolen devices.
MS-ISDN (Mobile Station International Subscriber Directory Number):
Definition: The actual phone number linked to a SIM card.
Use: Routing calls and messages to the intended subscriber.
Q.2(b) What is GPRS? How is billing and charging done in GPRS? (4 Marks)
Definition:
GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) is a packet-switching technology used in 2G and 3G networks to provide wireless data services like internet browsing, email, and MMS.
Features:
Provides always-on connectivity.
Enables efficient use of network resources through packet-switching.
Data speeds range from 56 kbps to 114 kbps.
Supports applications like online gaming and multimedia messaging.
Billing and Charging:
Volume-Based Billing:
Users are charged based on the data consumed (e.g., MB or GB).
Flat-Rate Plans:
Fixed monthly fees for unlimited or capped data usage.
Session-Based Billing:
Charges are applied for each active session, irrespective of data usage.
Postpaid and Prepaid Models:
Postpaid plans generate monthly bills; prepaid users are charged from their balance.
Uses:
Accessing web applications like browsing and email.
Enabling IoT devices for real-time communication.
Q.2(c) Define channel capacity. Write Shannon and Nyquist capacity formulas. State the key factors that affect channel capacity. (7 Marks)
Definition:
Channel capacity is the maximum rate at which data can be transmitted over a communication channel without significant errors.
Features:
Determines efficiency of communication systems.
Depends on bandwidth, signal strength, and noise.
Guides the design of telecommunication systems.
Shannon Formula:
C = B ⋅ log2(1 + SNR)
Where:
C: Channel capacity (bits per second).
B: Bandwidth (Hz).
SNR: Signal-to-Noise Ratio.
Nyquist Formula:
C = 2B ⋅ log2(M)
Where:
M: Number of distinct signal levels.
B: Bandwidth (Hz).
Key Factors Affecting Capacity:
Bandwidth: Higher bandwidth increases capacity.
Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR): Improved SNR enhances data rate.
Encoding Techniques: Better encoding allows efficient data transmission.
Interference: Reduces channel efficiency.
Uses:
Determines network performance.
Helps in wireless communication planning.
Optimizes data rates in digital systems.
Q.2 (C)What is fading? Differentiate
i. Fast and slow fading
ii. Flat and selective fading.
(OR)(7 Marks)
Definition:
Fading is the variation in signal strength caused by environmental factors like obstacles, reflection, or mobility. It affects the reliability of wireless communication.
| Aspect | Fast Fading | Slow Fading |
|---|---|---|
| Duration | Short periods. | Long periods. |
| Cause | Rapid changes (e.g., user movement). | Large obstacles (e.g., buildings, terrain). |
| Effect on Signal | Affects individual symbols or packets. | Impacts entire communication sessions. |
| Aspect | Flat Fading | Selective Fading |
|---|---|---|
| Frequency Impact | Affects all frequencies equally. | Impacts specific frequencies.. |
| Signal Bandwidth | Signal bandwidth less than Channel bandwidth. | Signal bandwidth greter than Channel bandwidth.. |
| Effect | Uniform attenuation. | Varies across different frequencies. |
Q.3(a) What is the hidden terminal problem? How can it be avoided? (3 Marks)
Definition:
The hidden terminal problem occurs in wireless networks when two devices cannot directly detect each other but try to send data to a common receiver simultaneously, causing collisions.
Features:
Common in wireless networks like Wi-Fi and ad hoc systems.
Leads to reduced network efficiency and increased retransmissions.
Avoidance Techniques:
RTS/CTS (Request to Send/Clear to Send): Devices reserve the medium before transmission.
Carrier Sense Multiple Access (CSMA): Devices check the medium’s availability.
Directional Antennas: Minimize interference by focusing signals.
Q.3(b) Write a short note on Selective Repeat ARQ. (4 Marks)
Definition:
Selective Repeat ARQ (Automatic Repeat Request) is an error-control protocol where only erroneous frames are retransmitted, not the entire sequence.
Features:
Allows multiple frames to be sent before receiving acknowledgment (ACK).
Uses sliding windows to track sent and acknowledged frames.
Ensures efficient use of bandwidth by reducing redundant transmissions.
 source:tutorialspoint
source:tutorialspoint
How It Works:
The sender keeps a window of frames it transmits.
If an error is detected in a frame, the receiver sends a negative acknowledgment (NAK).
Only the specific frame is retransmitted.
Example:
Sender transmits frames 1–5. If frame 3 is corrupted, only frame 3 is retransmitted instead of all frames.
Advantages:
Minimizes retransmissions.
Efficient for high-latency networks.
Limitation:
Requires more buffer memory to store transmitted and received frames.
Q.3(c) Discuss the network elements in GPRS that are different from GSM. Also discuss applications and limitations of GPRS. (7 Marks)
Network Elements in GPRS (vs. GSM):
Serving GPRS Support Node (SGSN): Handles mobility management, session management, and billing for packet data.
Gateway GPRS Support Node (GGSN): Acts as an interface to external packet-switched networks like the Internet.
PCU (Packet Control Unit): Handles packet data traffic between mobile devices and the core network.
Applications of GPRS:
Internet browsing and email access.
Multimedia Messaging Service (MMS).
Mobile applications like GPS and real-time gaming.
Limitations of GPRS:
Lower data speeds compared to modern technologies.
Latency issues due to shared resources.
Inefficient for high-bandwidth applications.
Conclusion:
GPRS enhances GSM by enabling data services, bridging the gap between 2G and 3G, but it has been replaced by advanced technologies like LTE due to its limitations.
Q.3 OR (a) Explain the Wireless Session Protocol Primitives and Parameters. (3 Marks)
Definition:
Wireless Session Protocol (WSP) is a part of the WAP (Wireless Application Protocol) suite, enabling session management for wireless devices to efficiently communicate over the internet.
Features:
Lightweight to suit resource-constrained devices.
Provides mechanisms for session initiation, data exchange, and termination.
Primitives:
Connect and Disconnect: Establish and terminate sessions.
Push and Pull: Allow client and server interactions.
Error Reporting: Handle session errors effectively.
Parameters:
Session ID: Unique identifier for tracking sessions.
Timeouts: Manage session inactivity.
Data Encoding: Optimize message transmission.
Q.3 OR (b) Define the term Multiplexing. Explain FDM and TDM with one example each. (4 Marks)
Definition:
Multiplexing is a technique to combine multiple signals into a single transmission medium, improving resource utilization.
 source:geeksforgeeks
source:geeksforgeeks
FDM (Frequency Division Multiplexing):
 source:geeksforgeeks
source:geeksforgeeks
How It Works:
Divides the bandwidth of the communication medium into non-overlapping frequency bands.
Each signal is modulated onto a separate frequency band.
Example:
Radio broadcasting where different channels use different frequency bands.
Advantages:
Simultaneous data transmission.
Limitation:
Limited by the available bandwidth.
TDM (Time Division Multiplexing):
 source:geeksforgeeks
source:geeksforgeeks
How It Works:
Allocates time slots to each signal in a cyclic manner.
Each user gets full bandwidth during their time slot.
Example:
Telecommunication systems where voice channels are interleaved in time.
Advantages:
Effective use of resources.
Limitation:
Delays if many users are active.
Q.3 OR (c) Draw and Explain the IEEE 802.11 Architecture in Detail. (7 Marks)
Definition:
The IEEE 802.11 architecture provides the framework for wireless local area networks (WLANs). It defines components and protocols for communication.
Features:
Supports both infrastructure and ad hoc modes.
Enables secure and scalable wireless communication.
Components of IEEE 802.11 Architecture:
Stations (STAs): Devices like laptops or phones equipped with wireless adapters.
Access Points (APs): Bridge wireless and wired networks, managing communication in the Basic Service Set (BSS).
Basic Service Set (BSS): A group of STAs communicating with one AP.
Extended Service Set (ESS): Multiple BSS interconnected via a Distribution System (DS).
Distribution System (DS): Facilitates communication between different APs in an ESS.
Diagram: 
source:slideshare
Applications:
Provides wireless internet access in offices, homes, and public spaces.
Enables connectivity for IoT devices.
Limitations:
Susceptible to interference.
Limited range compared to wired networks.
Q.4(a) Write a note on Transmission Media. (3 Marks)
Definition:
Transmission media is the physical path through which data is transmitted from one device to another in a network.
Types of Transmission Media:
Wired Media: Includes twisted pair cables, coaxial cables, and fiber optics.
Wireless Media: Uses electromagnetic waves, such as radio waves and microwaves.
Uses:
Facilitates communication over short and long distances.
Provides the foundation for both wired and wireless networks.
Q.4(b) Discuss DECT Frame Format. (4 Marks)
Definition:
DECT (Digital Enhanced Cordless Telecommunications) is a wireless standard used for voice and data communication in cordless phones.
DECT Frame Format:
Preamble: Synchronization and framing information.
A-field: Address field containing information like the device ID.
B-field: Data payload for voice or other communication.
C-field: Control field for signaling and error control.
Features:
Frame duration is typically 10 ms.
Uses TDMA for efficient spectrum utilization.
Applications:
Cordless telephony in homes and businesses.
Data communication for IoT devices.
Advantages:
Secure and reliable communication.
Operates in unlicensed frequency bands.
Limitations:
Limited to short-range communication.
Competes with other devices in the same frequency band.
Q.4(c) Explain Mobile IP. (7 Marks)
Definition:
Mobile IP (Internet Protocol) is a communication protocol designed to enable mobile devices to move between networks while maintaining a permanent IP address.
Features:
Provides seamless connectivity for mobile users.
Supports both IPv4 and IPv6.
Works by using home and foreign agents for packet delivery.
Components:
Mobile Node (MN): A device that moves between networks, like a smartphone or laptop.
Home Agent (HA): A router in the home network that tracks the MN's location and forwards packets.
Foreign Agent (FA): A router in the visited network that provides temporary care-of address (CoA) to the MN.
Correspondent Node (CN): A device communicating with the MN.
 source:geeksforgeeks
Working of Mobile IP:
source:geeksforgeeks
Working of Mobile IP:
When the MN moves to a foreign network, it registers with the FA and obtains a CoA.
The HA tunnels packets to the CoA using encapsulation.
The FA decapsulates packets and delivers them to the MN.
Outgoing packets are sent directly from the MN to the CN.
Advantages:
Ensures uninterrupted service during mobility.
Supports real-time applications like VoIP.
Limitations:
Overhead due to encapsulation and tunneling.
Potential delays in handover between networks.
Applications:
Enables mobile internet access for devices in motion.
Used in IoT devices requiring constant connectivity.
Q.4 OR (a) Write a note on Piconet and Scatternet. (3 Marks)
Definition:
Piconet: A small Bluetooth network consisting of one master and up to seven active slaves.
Scatternet: A collection of interconnected piconets where devices participate in multiple piconets as masters or slaves.
Features:
Piconet:
Simple topology.
Short-range communication.
Scatternet:
Complex but supports more devices.
Allows multiple connections.
Uses:
Piconet: Headphones, keyboards, and other peripherals.
Scatternet: Multi-device setups like smart homes.
Q.4 OR (b) Differentiate between GSM and GPRS. (4 Marks)
| Feature | GSM | GPRS |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Global System for Mobile Communication. | General Packet Radio Service. |
| Data Type | Circuit-switched for voice. | Packet-switched for data. |
| Speed | 9.6 kbps. | Up to 171.2 kbps. |
| Applications | Voice calls, SMS. | Internet access, MMS, email. |
| Connectivity | Always on for voice. | Always on for data. |
Q.4 OR (c) Draw and Explain Bluetooth Protocol Architecture. (7 Marks)
Definition:
Bluetooth protocol architecture defines layers and protocols used to manage Bluetooth communication effectively.
Architecture Layers:
Radio Layer: Handles physical transmission using radio frequencies.
Baseband Layer: Manages connection establishment and packet formatting.
Link Manager Protocol (LMP): Ensures security and connection control.
Host Controller Interface (HCI): Provides communication between hardware and software.
Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP): Handles multiplexing and segmentation.
Application Layer: Runs user-level applications like file transfer and audio streaming.
Diagram:  source:geeksforgeeks
source:geeksforgeeks
Applications:
Wireless peripherals like headphones and keyboards.
File sharing between devices.
Limitations:
Limited range of around 10 meters.
Potential interference from other devices.
Q.5(a) Shortly explain handover in GSM. (3 Marks)
Definition:
Handover in GSM refers to transferring an active call or data session from one cell or channel to another without interruption.
Types of Handover:
Intra-Cell: Within the same base station.
Inter-Cell: Between different base stations.
Inter-BSC: Between base station controllers.
Inter-MSC: Between mobile switching centers.
Uses:
Ensures uninterrupted communication during mobility.
Improves network resource utilization.
Q.5(b) Describe Error Control Coding in detail. (4 Marks)
Definition:
Error Control Coding is a method to detect and correct errors in transmitted data, ensuring reliable communication.
Types:
Error Detection: Identifies errors using methods like parity checks.
Error Correction: Corrects errors using redundancy.
Techniques:
Parity Bits: Adds an extra bit to indicate error presence.
Hamming Codes: Corrects single-bit errors by adding parity at multiple positions.
Cyclic Redundancy Check (CRC): Uses polynomial division for error detection.
Applications:
Wireless communication.
Data storage systems.
Q.5(c) Define Android layout. Explain various Android layouts. (7 Marks)
Definition:
An Android layout defines the visual structure of a user interface for an application, specifying the arrangement of UI components.
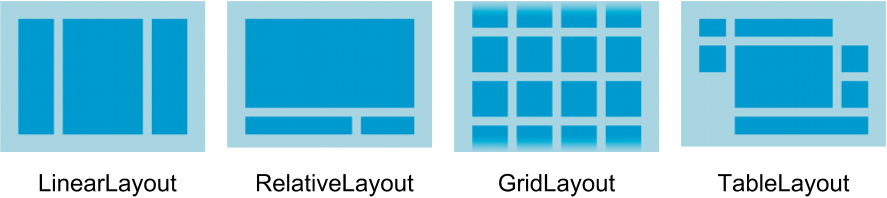
Types of Android Layouts:
Linear Layout:
Aligns child views in a single direction (horizontal or vertical).
Example: A vertical list of text boxes.
Relative Layout:
Positions elements relative to each other or parent.
Example: Placing a button below a text field.
Constraint Layout:
Allows complex layouts with constraints to parent or sibling elements.
Example: A responsive screen design.
Frame Layout:
Stacks child views on top of each other.
Example: Overlaying a loading icon on an image.
Table Layout:
Arranges elements in rows and columns.
Example: A form with labels and text fields.
Advantages:
Provides flexible UI design options.
Supports responsive designs for different screen sizes.
Conclusion:
Choosing the right layout depends on the application's complexity and user experience goals.
Q.5 OR (a) What are HLR and VLR? Describe its functions in Call Routing and Roaming. (3 Marks)
HLR (Home Location Register):
Definition: HLR is a central database in mobile networks that stores permanent information about subscribers, such as their phone numbers, service preferences, and current location.
Functions:
- Stores the subscriber's profile, including authentication and billing details.
- Provides location information to the network during call routing.
- Responsible for managing the subscriber’s services (voice, SMS, etc.).
VLR (Visitor Location Register):
Definition: VLR is a temporary database that stores information about subscribers who are currently in the area served by a particular mobile network.
Functions:
- Acts as a cache for subscriber data from HLR for local operations.
- Assists in call routing by storing information about subscribers within its coverage area.
- Manages temporary data such as current location, service status, and authentication.
Call Routing and Roaming:
- When a user roams, the VLR communicates with the HLR to obtain the necessary details of the subscriber’s profile and location.
- Call Routing: If a call is placed to a roaming subscriber, the VLR forwards the request to the HLR, which routes the call to the appropriate visited network based on the location information.
Q.5 OR (b) Shortly explain 1G, 2G, 2.5G, and 3G Mobile Communications. (4 Marks)
| Generation | Technology | Data Speed | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1G | Analog systems (AMPS, NMT) | 2.4 kbps | - Only voice communication. - No encryption, prone to interference. |
| 2G | Digital systems (GSM, CDMA) | 50-100 kbps | - Introduced digital signals. - Enabled SMS and basic data transfer. |
| 2.5G | GPRS (General Packet Radio Service) | 144 kbps | - Enabled packet-switched data services. - Better data rate than 2G. |
| 3G | UMTS, CDMA2000 | 384 kbps - 2 Mbps | - Supports video calls, high-speed internet. - Introduced mobile broadband. |
Q.5 OR (c) Explain Android Application Framework with its components. (7 Marks)
Definition:
The Android Application Framework provides a set of APIs for building applications on the Android platform. It is the foundation for creating and managing the core functionality of Android apps.
Components of the Android Application Framework:

source:javatpoint
1) Linux kernel:
It is the heart of Android architecture that exists at the root of Android architecture. Linux kernel is responsible for device drivers, power management, memory management, device management, and resource access.
2) Native Libraries:
On top of the Linux kernel, there are Native libraries such as WebKit, OpenGL, FreeType, SQLite, Media, C runtime library (libc), etc.
- The WebKit library is responsible for browser support.
- SQLite is for database management.
- FreeType is used for font support.
- Media handles playing and recording audio and video formats.
3) Android Runtime:
In the Android runtime, there are core libraries and DVM (Dalvik Virtual Machine) that are responsible for running Android applications. DVM is similar to JVM but optimized for mobile devices. It consumes less memory and provides fast performance.
4) Android Framework:
On top of Native libraries and Android runtime, there is the Android framework. The Android framework includes Android APIs such as UI (User Interface), telephony, resources, locations, content providers (data), and package managers. It provides many classes and interfaces for Android application development.
5) Applications:
On top of the Android framework, there are applications. All applications such as home, contact, settings, games, and browsers are built using the Android framework that utilizes Android runtime and libraries. Android runtime and native libraries depend on the Linux kernel.
Activities:
- Represents a single screen with a user interface.
- It allows interaction with the user and manages the flow of screens in an app.
Services:
- A component that runs in the background, performing long-running operations.
- Examples: Music playing, downloading files.
Content Providers:
- Allows data sharing between applications.
- Example: Accessing contacts or media files from other apps.
Broadcast Receivers:
- Used for listening to and responding to system-wide broadcast messages.
- Example: Receiving notifications for incoming messages or network changes.
Intents:
- Messaging objects used for communication between components like Activities, Services, etc.
- Example: Starting a new Activity or sending a broadcast message.
Views and ViewGroups:
Views: Basic UI elements like buttons, text fields, etc.
ViewGroups: Containers that hold and manage views (like LinearLayout, RelativeLayout).
Key Features:
- Provides modular architecture for app development.
- Allows handling user interface, background processes, and data management efficiently.
- Enables component-based development, where each feature of an app is managed by different components.
Advantages:
- Reusable components that save development time.
- Seamless integration of UI and non-UI functionalities.
- Facilitates multitasking and background operations in Android apps.


0 Comments